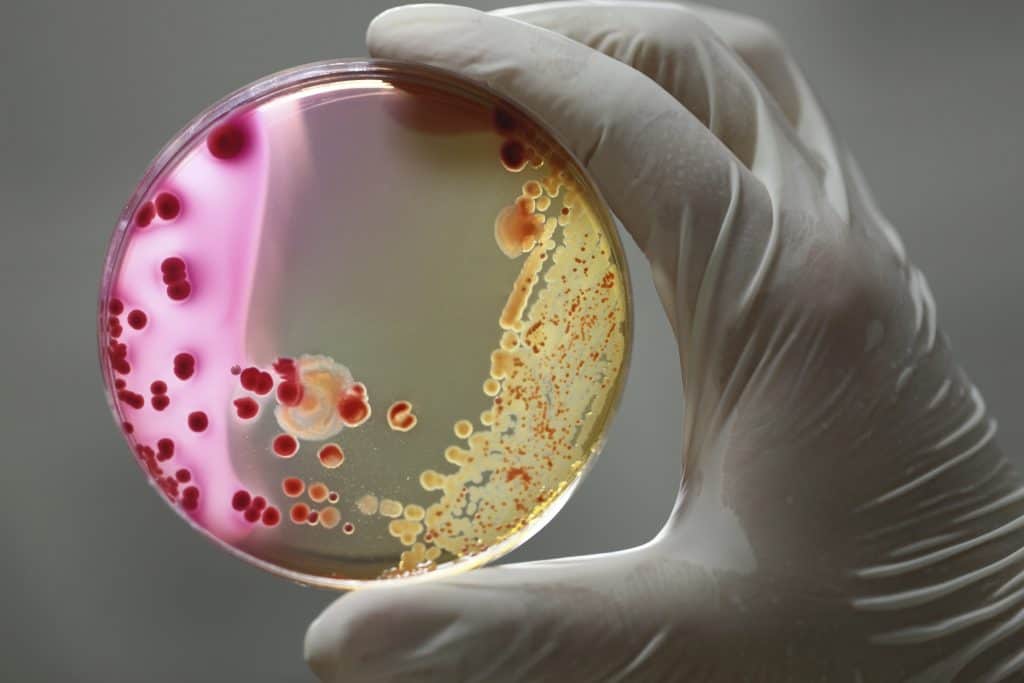

Skin infection overview: staph infection.
Most people have heard about staph infections, often through queasiness-inducing stories of medical mishaps. Many also known that the bacteria responsible, Staphylococcus Aureus, is resistant to commonly-used antibiotics (and becoming more so every year).
Staph infections can indeed become life-threatening emergencies. Yet it’s also true that about 25% of normal, healthy people carry S. Aureus in their mouth, nose, or genitals. This potentially deadly organism causes these individuals to experience no symptoms whatsoever.
Staph infection foot
Staph is also commonly found on the feet. They provide a warm, moist environment for the bacteria, and they’re in frequent contact with the dirty floor. Furthermore, diabetic feet often have a poor blood supply and are more prone to infections. It’s no surprise that podiatrists are quite familiar with treating staph infections of all severity levels. Patients with compromised immune systems due to disease or the side-effects of prescription medications are also particularly vulnerable.
Infection with S. Aureus can take on several different forms. It’s relatively easy for these bacterial organisms to enter small cuts on the feet. The surrounding skin then typically takes on a distinctive “honey-yellow crusted” appearance. Most staph infections of the feet are minor, and some need no treatment beyond sterile dressings and antibiotic ointment.
Flesh Eating Bacteria
All have the potential to become much more severe if treatment is needed but not received, however. The severity of a staph infection is mostly determined by its depth and relative strength. Extremely deep or extensive infections can literally become “flesh eating.” This non-technical term refers to the extensive tissue damage these life-threatening staph infections can cause. Immediate treatment is required in all cases where a staph infection is causing necrosis (tissue death).
The infection can also appear as one of various types of boils. Another common (and often treatment-resistant) form is known as cellulitis. This involves the infection of the deepest layers of the skin, and requires antibiotics to treat effectively. If the variety of S. Aureus responsible is resistant to potent prescription antibiotics the situation can quickly become serious.
Best Treatment for Wounds with a Staph Infection
What is dermaPACE?
If you have any wound dressings or bandages, the staff will first remove them. The wound will be photographed and measured to later evaluate progress. We will then gently clean the area and apply a sterile gel to the wound. The treatment will begin by delicately placing the dermaPACE applicator on the surface of the wound. You will notice an audible “popping” sound coming from the device for the duration of the treatment. In most cases, you will require only a few treatments that last less than 15 minutes. This, of course, will depend on the location of the wound, the wound’s size, your overall health and other factors. After the treatment is completed, you will want to rebandage your wound. Your healthcare provider will give you instructions on aftercare. Healing and recovery time both improve when you become an active participant in your wound care.

Are There Side Effects or Complications?
There are minimal risks associated with using the dermaPACE. It can cause redness, slight bruising or a sensation of tingling and numbness in some cases. These side effects are generally short lived and go away on their own. There may be in brief increase to the amount of pain that is felt right after the treatment. Again, this will go away shortly.
Can Home Remedies Cure Staph Infection?
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil, an essential oil that can help with everything from pimples to acne scars, has also been shown to be effective in treating staph infections.
This essential oil contains antibacterial and anti-inflammatory characteristics that aid in the treatment of staphylococcus bacteria-related skin infections.
Tea tree is a bactericidal plant that inhibits Bavaria growth and lessens the effects of staph infection.
Turmeric
Turmeric is a powerful antibiotic and anti-inflammatory substance that can help you fight staph infections.
Curing the illness with a tonic comprised of turmeric powder, black pepper, water, and coconut oil taken several times a day is effective.
To relieve pain and redness, mix turmeric powder with lime powder and water and apply as a paste to the affected area. It lowers infection by drying up the pus in the blister.
Want More Information on Staph Infections and treatments?
If you have questions or concerns about the dermaPACE procedure, take the time to talk to your Podiatrist. She should be able to tell you if dermaPACE procedures can help with your healing. Our staff has been professionally trained and have extensive, first-hand experience in using dermaPACE.
Call 878-313-3338
Our lead development product for the global wound care market, dermaPACE, has been CE Marked for use on acute and chronic defects of the skin and subcutaneous soft tissue.
Staph infection signs & symptoms.
Staph cellulitis is probably the most commonly encountered staph infection of the skin. Like other forms, it has the potential to become quite serious if not treated with antibiotics.
It isn’t obvious in all cases exactly where a staph cellulitis begins. Signs of inflammation (swelling, redness, tenderness, and warmth) may begin to appear in a small-medium area overlying the infection. This can be the only warning that an active infection in its early stages is present.
A small cut, sore, or ulcer is visible from the start in other situations, however. This is usually located at or near the infection’s center. Bodily symptoms, such as fever, chills / sweats, will likely be present in moderate-severe cases.
Other forms of infection include impetigo, a highly uncomfortable reddish rash. It presents with distinctive looking clusters of usually raised sores. Young children can also contract a condition called “Scalded Skin Syndrome.” This is actually a type of S. Aureus infection which can mimic the signs and symptoms of heat-damaged skin.
How are staph infections of the skin treated?
This has manifested in gradual changes in how well commonly prescribed antibiotics work. Penicillin used to be the antibiotic of choice for most varieties of staph infection in recent decades. Many staph species became less and less sensitive to penicillin, and as a result drugs such as methicillin were used.
Today species such as Methicillin-Resistant Staph Aureus are appearing in environments where antibiotics are used the most extensively—hospitals. This is a doubly dangerous, since some hospital inpatients have compromised immune systems.
Fortunately, physicians still have stronger antibiotics which remain effective against all staph organisms. This includes MRSA and other particularly aggressive or hardy varieties. The situation calls attention to the ongoing problem of antibiotic-resistant organisms and the dangers of irresponsible antibiotic use, however.
Can staph infections lead to more severe health conditions?
Yes, staph infections can potentially lead to more severe health conditions, especially if left untreated or if they become invasive. While many staph infections are minor and can be treated effectively with antibiotics, certain circumstances may increase the risk of complications:
- Abscess Formation: Staph infections can cause the formation of abscesses, which are pockets of pus. If these abscesses are not drained and treated promptly, they can lead to more extensive tissue damage and complications.
- Bone and Joint Infections: Staph bacteria can invade bones and joints, leading to serious conditions such as osteomyelitis (bone infection) or septic arthritis. These infections may require surgical intervention and prolonged antibiotic therapy.
- Bloodstream Infections: Staph infections can enter the bloodstream, causing bacteremia. If the bacteria spread to other organs, it can result in more severe conditions, such as endocarditis (infection of the heart valves) or sepsis, a life-threatening systemic response.
Can animals transmit staph infections to humans?
Yes, animals can potentially transmit staph infections to humans. Staphylococcus bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, which commonly causes staph infections in humans, can be present on the skin and mucous membranes of various animals. While transmission from animals to humans is not as common as person-to-person transmission, it can occur under certain circumstances.
Factors contributing to potential transmission:
- Close Contact: Close contact with animals, especially if they have skin infections or are carriers of Staphylococcus, increases the risk of transmission.
- Compromised Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems may be more susceptible to infections, including those transmitted from animals.
Preventive measures:
- Hand Hygiene: Thorough handwashing after handling animals is crucial to prevent the transfer of bacteria to the mouth, nose, or eyes.
- Avoiding Contact with Sick Animals: If an animal is visibly ill or has skin lesions, it’s advisable to avoid direct contact until the animal has been treated.


